MEASURES - What do over 500 dams within protected areas mean for migratory fish?
13-08-2020
Dams are one of the main factors in the 76% collapse in freshwater migratory fish populations since 1970.
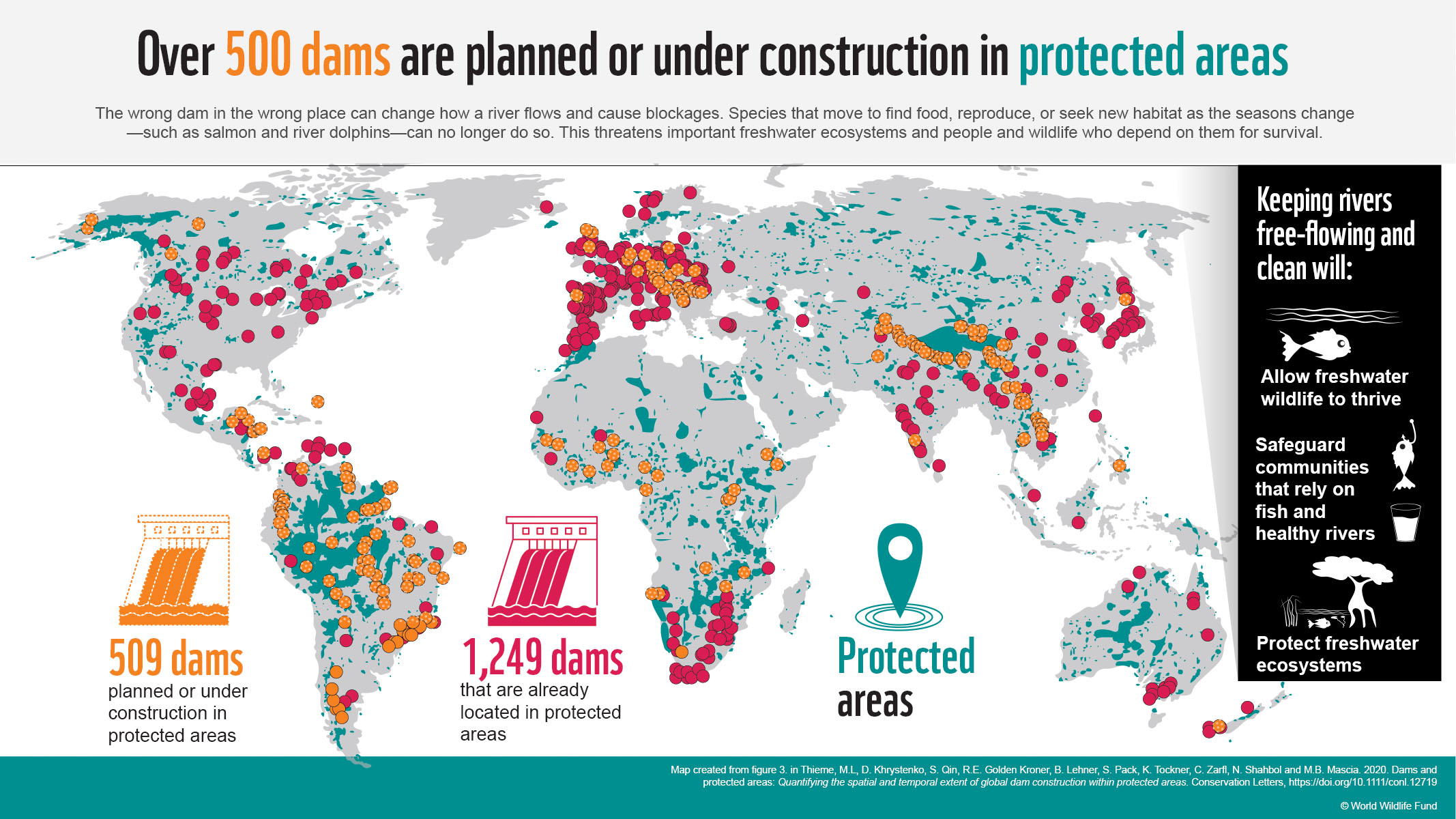
More than 500 dams are planned or under construction within protected areas, according to a new study published in Conservation Letters. These findings raise red flags as dams can have detrimental impacts on livelihoods of local communities such as fishing and floodplain farming, species movements, sediment flows to downstream deltas and floodplains, and other critical river functions. What is more, the study supports the importance of conservation projects that focus on restoring the ecological aquatic corridors for migratory fish species, such as the MEASURES project. This aims to develop and test a methodology for mapping migratory fish habitats, a first step towards restoring ecological corridors.
“Rivers are the lifeblood of ecosystems. Any policy that aims to conserve nature must prioritize the free flow of rivers,” said Michele Thieme, lead author of the study and lead freshwater scientist at World Wildlife Fund (WWF). “Protected areas are a fundamental strategy for conserving biodiversity and services to people, but their design and management to protect freshwater ecosystems must be improved.”
Freshwater biodiversity is declining dramatically. Populations of freshwater vertebrates (mammals, wetland birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish) have seen an 83% decline between 1970 and 2014. One of the primary drivers of this decline are dams and other water infrastructure that impact the natural habitats of freshwater species like river dolphins, otters, migratory fish and tens of thousands of other species.
The paper also finds that over 1,200 large dams already exist within protected areas. Almost three-quarters (907) of these dams were built before protected area establishment. Anecdotal cases suggest that protection may be put in place to prevent sediment from filling the reservoir and affecting energy or water supply, as well as recreational opportunities on the artificial lake created by the reservoir.
There are also instances of governments redefining the boundaries of protected areas, and activities permitted within them, to legalize the construction of a dam within an existing protected area. When regulations on protected areas are loosened in such a way, protected areas lose their ability to conserve ecosystems.
This study comes at a time when the adverse impacts of dams and reservoirs are clearer than ever. A 2019 paper published in Nature finds that over two-thirds of long rivers are impeded by dams and infrastructure. Dams fragment rivers and affect the diverse benefits that healthy rivers provide to people and nature across the globe. According to a recent report, dams are one of the main factors in the 76% collapse in freshwater migratory fish populations since 1970.
