CD SKILLS Improving celiac disease management in the Danube region by raising the awareness, improving the knowledge, and developing better skills
Pilot projects
New innovative services are needed in order to improve public healthcare service and quality of life of celiac disease patients, as the existing Celiac disease management practices are insufficient in the Danube region. New services were identified and organised into seven pilot projects:
- Testing for Celiac disease in general population, risk groups and elderly
- Testing for Celiac disease related complications
- ICT supported histopathology analysis of biopsy samples
- Patient registry set-up
- Monitoring of CD patients with telemedicine solutions
- Development and implementation of gluten-free products registry.
- Improved capacity of food catering providers to provide safe gluten-free products
The work related to the implementation of the pilot projects is grouped in the following activities:
Activity A.T4.1 - Identification of pilot services, creation of stakeholders groups and preparation of common pilot methodology
Activity A.T4.2 - Implementation of pilot services aiming at early and accurate diagnosis and detection of complications
Activity A.T4.3 - Implementation of pilot services aiming at improving the quality of life of CD patients;
Activity A.T4.4 - Preparation of common pilot activity report including recommendations for transfer to other regions.
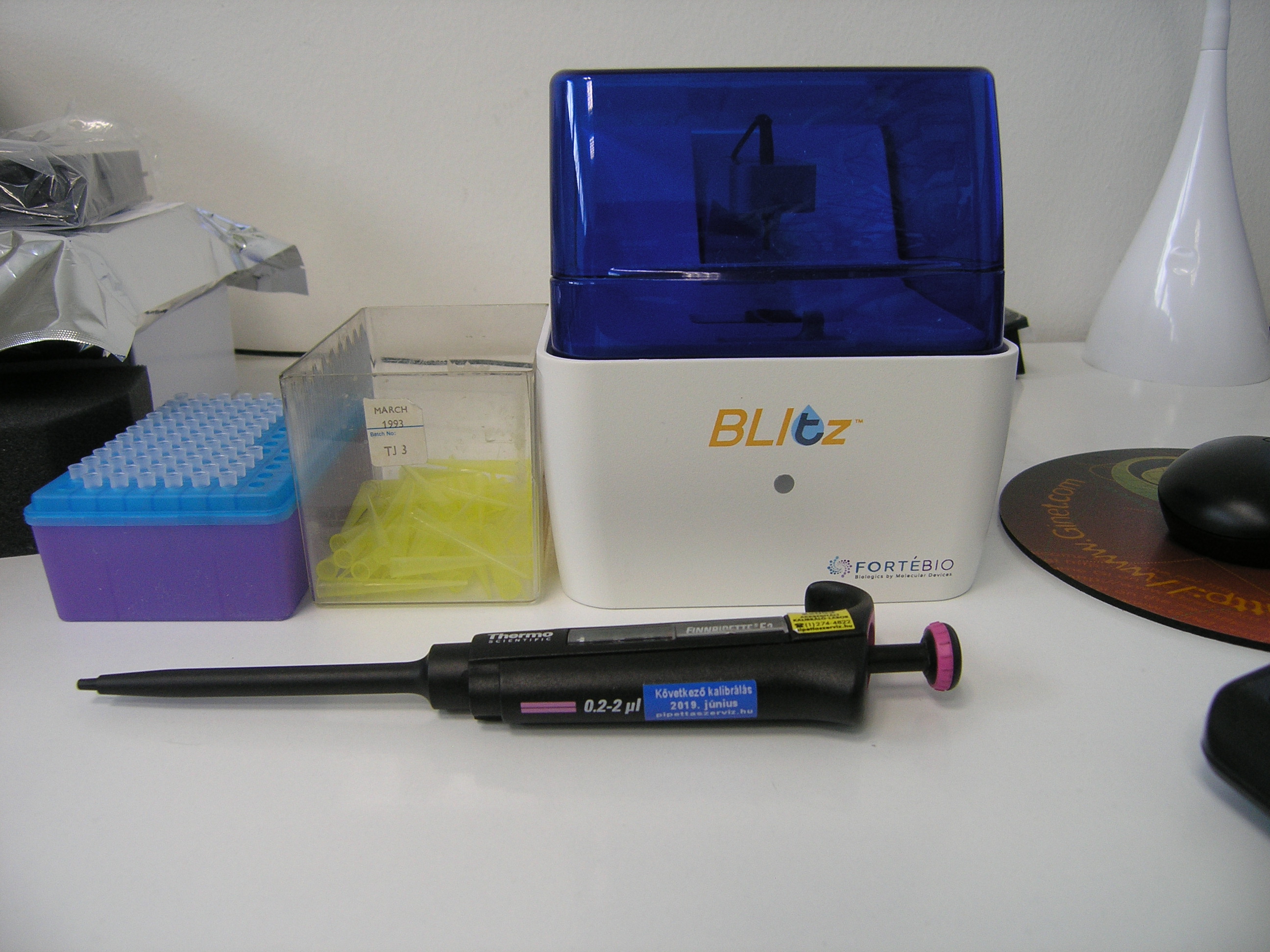
A new BLItz Technology-based instrument to assist near-patient quantitative measurement of celiac antibodies (pilot No.3 - ICT supported histopathology analysis of biopsy samples).
PILOT No 1: Testing for Celiac disease in general population, risk groups and elderly
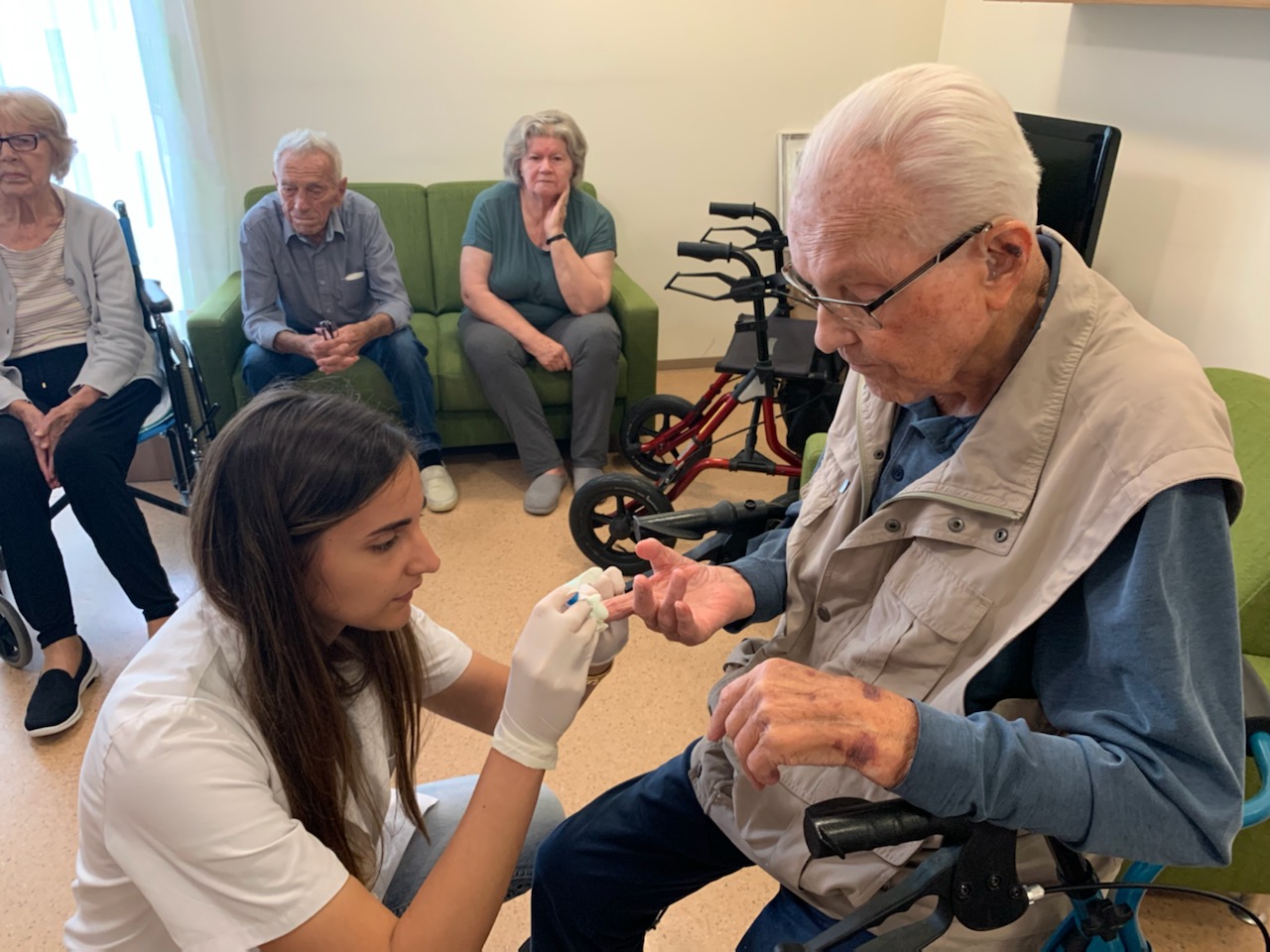
Many CD patients are diagnosed with substantial delay, with serious implications on their health and overall quality of life. Undetected patients are exposed to risk for development of serious complications of the disease including osteoporosis, thyroid disease, anaemia, infertility, etc. In order to detect patients early in the course of disease rapid finger prick blood tests will be used which are less invasive than conventional tests, are sufficiently reliable, enable fast detection and cost less. Specific groups will be tested based on partners needs. We intend to include first-degree relatives, students, and elderly in this activity. Rapid tests require minimal quantity of blood and provide a reliable resulrts in 5-10 minutes. All participants suspected of having CD will be invited for confirmatory tests.

PILOT No 2: Testing for Celiac disease-related complications due to either late diagnosis or long-term poor compliance
The pilot project “Testing for Celiac disease-related complications due to either late diagnosis or long-term poor compliance” was conducted in order to give us information on how to monitor the patient with celiac disease (how often to do serology in order to monitor compliance to a gluten-free diet, when it is necessary to repeat endoscopy and biopsy, which parameters need to be controlled and how often for the rest of life....)
From several points of view, celiac disease patients could reveal complications:
- delay in diagnosing celiac disease, sometimes for years
- non-adherence to a strict gluten-free diet
- adherence to a strict gluten-free diet, but without consultation with a nutritionist, which increases the risk of malnutrition
In order to do address these issues, patients participating in this pilot were divided into three groups:
- newly diagnosed patients with celiac disease
- patients on a strict gluten-free diet for more than six months, with good compliance (according to Biagi score)
- patients on a gluten-free diet for more than six months, with bad compliance (according to Biagi score)
After several meetings, the pilot project partners designed a questionnaire about symptoms and signs. For evaluation of compliance to a gluten-free diet, Biagi score was used. The laboratory tests that were used were: complete blood count, liver and kidney function test, albumins and proteins, parameters for anaemia, coagulation, minerals and vitamin status (vitamin D, B12, and folic acid), and bone mineral density scan (DEXA).
The data will be collected until the end of September 2022. After conducting this pilot project, we will prepare recommendations on a follow-up plan for celiac disease patients.
PILOT No 3: ICT supported histopathology analysis of biopsy samples
The pilot is addressing the challenges for an accurate diagnosis of celiac disease. Inadequate histopathology analysis of small biopsy samples and/ or misinterpreted results can lead to wrong diagnoses of celiac disease. One of the methods that could improve and facilitate the biopsy based diagnostic procedure is ICT supported histopathology analysis of biopsy samples that will be compared to traditional methods.
The specific objectives of the pilot are:
- to improve the inter-observer agreement between pathologists;
- to define and apply better ways, with higher precision for the histo-examinations especially in difficult cases;
- to decrease of number of cases with “unclear”, “inconclusive” diagnosis;
- to avoid misdiagnosis, solve most of the cases with conflicting results between the clinical and pathology data;
- to facilitate discussion of cases between pathologists and clinicians and between centres with different levels of experience in celiac disease.
The partners involved in this pilot are University Medical Center Maribor, Medical University of Graz, Children's Hospital Zagreb, National Institute for Mother and Child Health “Alessandrescu-Rusescu” Bucharest, Heim Pal National Paediatric Institute Budapest, and LMU University Hospital Munich.
PILOT No 4: Patient registry set-up
Across the Danube region, there is lack of good quality, standardized data regarding celiac disease patients. The objective of the pilot is to develop a common patient registry structure for aligned national registries. The registries would enable the collection and analysis of data for epidemiology, clinical presentation and characteristics of the disease, diagnostics, associated disease, complications and treatment. The information will enable also a better common management of celiac disease in the Danube region. This all together will improve the health care and the quality of life of patients with celiac disease.
The partners involved in this pilot are University Medical Center Maribor, University Children's Hospital Belgrade, Children's Hospital Zagreb, National Institute for Mother and Child Health“ Alessandrescu-Rusescu” Bucharest, CeliVita - Living with Celiac Disease Zagreb, Heim Pal National Paediatric Institute Budapest, “Nicolae Testemitanu” State University of Medicine and Pharmacy of the Republic of Moldova, Chisinau, and LMU University Hospital Munich.
PILOT No 5: Monitoring of CD patients with telemedicine solutions
To limit the need for direct patient/doctor interaction, thus decreasing the exposure of both patients and HCPs to risk of infections, basic patient clinical and anthropometric data will be assessed remotely with the help of WiFi devices using telemedicine solutions. Data about the quality of life and dietary compliance will be analysed remotely and based on the results virtual meetings will be scheduled. Face-to-face visits will only be scheduled when some further interventions will be needed. Solution will be a basis for a proposal to include the telemedicine service to governing authorities and insurances.
PILOT No 6: Pilot Development and implementation of gluten-free products registry
The objective of the pilot is to protect the health of the coeliac patient by giving correct and “on time” information, through the development of a GF products registry that will serve not only to coeliac patients, but to everybody preparing strict GF food, providing correct and up to date information about gluten free products.
Despite the existing EU regulations, insufficient or wrong food information is still a great challenge for celiacs. Unintentional traces of gluten contamination are one of the biggest issues since food producers often put/miss putting statements about presence of gluten without real criteria.
Application is available here: https://bezglutena.celivita.hr/
GF product registry was developed as a "mobile first" web application, with user-friendly interface which will enable users to easily reach the information.
Pilot partners, celiac societies, will continue with the activities focused on data enrollment, with use of administrative web interface. Also, it will be important to establish good and continuous communication with relevant gluten free food producers, with the aim to maintain food information based on trustful sources and proofs.
Partners involved in the pilot project are: PP07 USZC and PP09 CeliVita.
PILOT No 7: Pilot Improved capacity of food catering providers to provide safe gluten-free products
The overall objectives of the pilot are:
- To raise awareness about celiac disease and strict gluten free diet
- To improve specific stakeholders’ (HORECA, hospitals, schools, kindergarten, elderly homes) capacities for preparation of GF food and their food information communication
- To protect physical and mental health of coeliacs and to improve quality of life of coeliacs and their families
During the first year of the project, 28 workshops were held with selected stakeholders. A register of stakeholders has been established to cover as many different groups as possible: institutions and caterers who prepare gluten-free food for their protégés or customers. The aim of the workshops was to get acquainted with the problems and challenges they face and the shortcomings in the field of knowledge and available information.

Information from the workshops will be used for further planning of an educational event for caterers and all those who prepare gluten-free food, which will be held virtually in early 2022. When asked what would help them to be able to prepare a gluten-free meal, most of the interviewees answered that a list of safe gluten-free products (gluten-free product register) would be of great help. Some of the other responses are: Assistance in identifying critical points and mitigation measures in the food production chain; Menus; Instructions for the preparation of gluten-free meals, Changes in public procurement procedures; Reliable food traceability; Staff education; Knowledge, young staff should be aware of severe symptoms; More staff; More space, separate space for preparing gluten-free food; Better equipment.
The Covid-19 pandemic crisis required our response, so we have adjusted our pilot activities to new circumstances. Our main event will be prepared live online and recorded, for further use.
Partners involved in the pilot project are: PP02 MOM, PP07 USZC, PP08 INSMC and PP09 CeliVita.