CD SKILLS - Assessing adherence to gluten-free diet - do we miss patients who occasionally eat gluten?
23-05-2022
At our center in Children's Hospital Zagreb, all newly diagnosed patients with celiac disease and their parents are seen by a dietitian who explains gluten-free diet and gives written information. After that, a patient is scheduled for regular follow-up visits by both pediatric gastroenterologist and dietitian.
At every follow-up visits we check serological parameters (tissue transglutaminase antibodies) and ask patients and their parents about adherence to gluten-free diet. Generally, we were satisfied having most of the families saying that they strictly follow gluten-free diet and most of the patients having normal serological parameters.
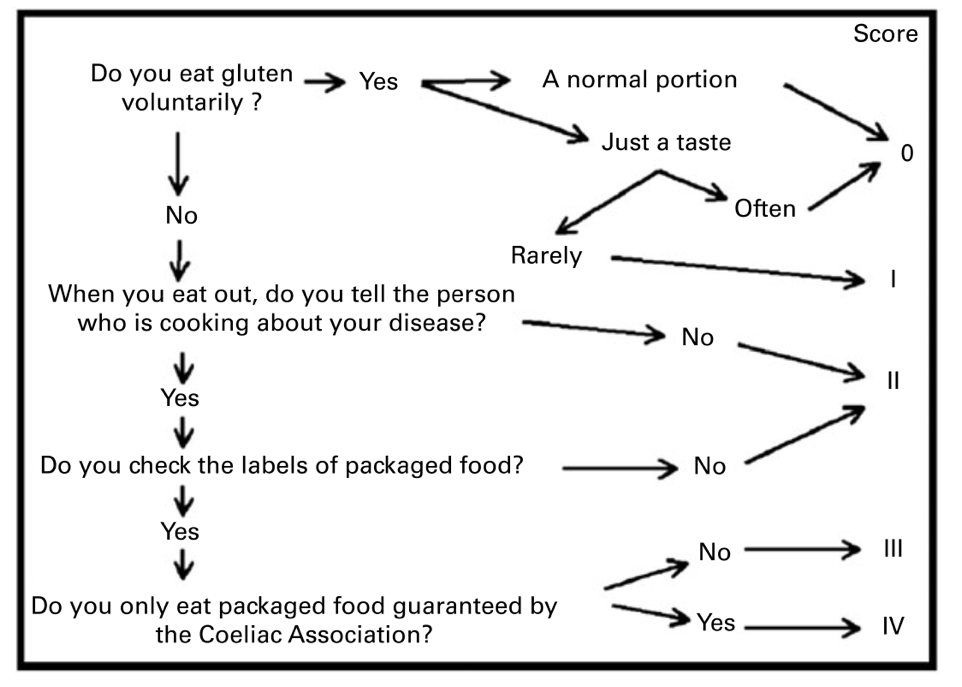
Within CD SKILLS pilot project on complications, we started to apply a gluten-free diet score developed by Biagi and collaborators (2009) to evaluate dietary compliance. The results surprised us unpleasantly. Among 74 consecutively seen patients in our pediatric gastroenterology clinic, 13 (18%) were not complying to gluten-free diet. Four of them eat gluten often, and the rest eat gluten only rarely. Eight of those non-compliant patients answered our routine question „Do you follow gluten-free diet? “ answered „yes“. However, when we applied Biagi's questionnaire we found out that the patients eat gluten from time to time at school, have „cheating days“once monthly or yearly or have some gluten snacks from time to time. Three of those patients had normal serology and could not have been otherwise recognized as non-adherent.
This is a small sample of patients, but it made us aware of the problem and the need to pay more attention in evaluating dietary compliance and of the necessity to continuously educate what does strict dietary compliance imply.